Are you planning a trip to Japan? While trains are a very convenient means of transportation in Japan, it is important to know the differences between the various types of train operations.
The fare, number of stops, comfort, and other factors vary depending on the type of train operation, such as limited express, rapid, express, semi-express, and local. This article will therefore explain in detail the differences between the different types of train service in Japan, limited express, rapid, express, semi-express, and ordinary.
JR tickets have a classification for children. Elementary school students and younger are charged half the adult fare.
Preschool children are classified as infants. If they sit on your lap and do not use a seat, there is no charge.
Elementary school students: 6 to 12 years old in Japan.
The name of the type of train varies depending on the railroad company. The following is a list of common train types in order of speed.
Shinkansen (Japanese spelling:新幹線)

Shinkansen is a high-speed train capable of reaching speeds of 200 km/h or more. They use unique rails and standards that are different from those of ordinary trains, and they use a variety of the latest technologies.
There are many Shinkansen lines throughout Japan.
- Kyushu Shinkansen
- Sanyo Shinkansen
- Tokaido Shinkansen
- Hokuriku Shinkansen
- Joetsu Shinkansen
- Tohoku Shinkansen
- Yamagata Shinkansen
- Akita Shinkansen
- Hokkaido Shinkansen.
To board a Shinkansen train, you need a boarding ticket and an express ticket. There are three types of limited express tickets: unreserved seats, reserved seats, and green cars.
Non-reserved seat(Japanese spelling:自由席)

You cannot select your seat in advance. If there is a vacant seat in a non-reserved seat car, you can sit down freely. Tickets can be purchased at a lower price than reserved seats.
On the day of purchase, you can board the Shinkansen at any time during the section of the ticket you purchased.
If the non-reserved seat car is full, you will not be able to sit in a seat, so you will have to stand.
Reserved seat(Japanese spelling:指定席)

You can select your seat in advance. You can be sure to be seated even when the train is crowded. It is easy to secure your preferred seat, such as a window or aisle seat.
If you miss your designated bullet train, your reserved seat ticket becomes invalid, but you can board a subsequent nonreserved seat.
Green Car(Japanese spelling:グリーン車)
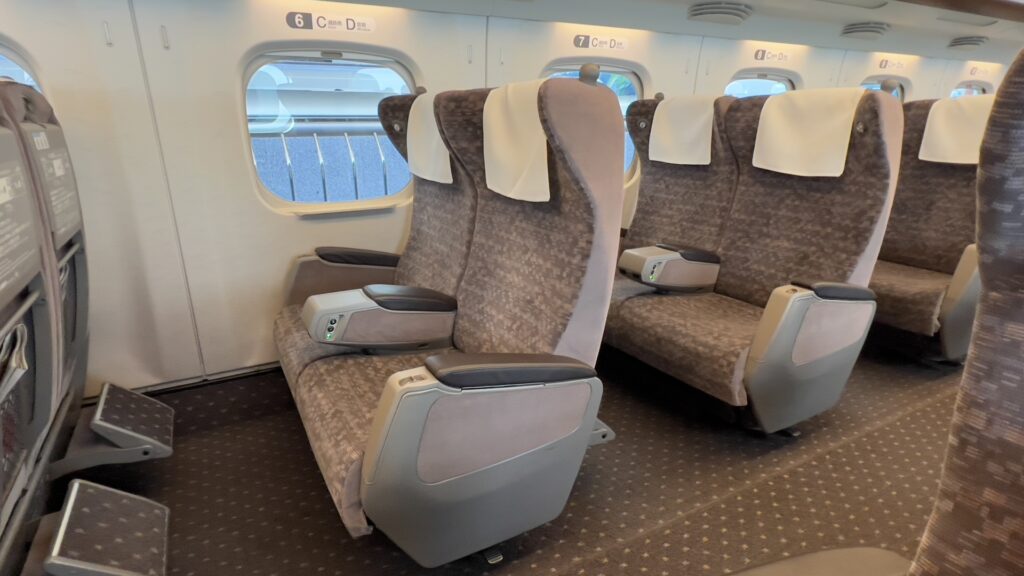

The Green Car is the highest class of Shinkansen cars. It is available in many Shinkansen cars and can be used by paying a green fare.
The seats are two-seater plus two-seater, with four seats side by side. The seat pitch is 1,160 mm, which is more spacious than that of a standard car (1,040 mm).
What is limited express?(Japanese spelling:特急)

Limited express is a shortened name for a special express train. It is a train that is at the higher level of express trains. It is a fast and comfortable train that connects major cities and tourist destinations.
Normally, seat reservations are required and an express fare is charged in addition to the boarding fee, while non-JR trains can be divided into two types: those that require an express fare and those that require only a regular fare.
Because they basically use the same rails as regular trains, the maximum speed is limited to about 130 km/h.
What is an express train?(Japanese spelling:急行)

An express train stops at even fewer stations than a rapid train, and only stops at major stations. Express trains stop at more stations than limited express trains.
What is “Kaisoku”?(Japanese spelling:快速)
A rapid train is one that stops at fewer stations along the way than a local train. These trains are often used for inter-regional travel.
Rapid trains serve to connect major stations with regional stations and are an important means of transportation for people in the region.
Since rapid trains stop at fewer stations than regular trains, they can run faster, making them a good choice for those who want to shorten their travel time. No special fare is charged.
Commuter Rapid and Commuter Express(Japanese spelling:通勤快速・通勤急行)
These are trains for commuters that operate during the morning and evening rush hours. The purpose of these trains is to ease congestion. Anyone can board.
What is a semi-express train?(Japanese spelling:準急)
A semi-express train is also called a semi-express train. It has more stops than the rapid and express trains, and is often used for travel within a region.
What is an ordinary train?(Japanese spelling:普通)

Normal is a train that stops at all stations on its route. Because it stops at many stations, it is not as fast as an express train.
Only a boarding ticket is required. These trains are often used as a means of transportation within the region. They are crowded during commuting hours.
The table below shows the differences between major companies.
| company | fastest-order |
|---|---|
| JR | Japanese spelling;特急>急行>通勤快速>快速>区間快速>普通 Limited Express > Express > Commuter Rapid > Rapid > Section Rapid > Ordinary |
| 東武鉄道 Tobu Railway | Japanese spelling;特急>急行>区間急行>準急>区間準急>普通 Limited express > express > sectional express > semi-express > sectional semi-express > ordinary |
| 京浜急行鉄道 Keihin Express Railway | Japanese spelling;ウイング号>エアポート快特>快特>特急>エアポート急行>普通 Wing > Airport Rapid Express > Rapid Express > Limited Express > Airport Express > Ordinary |
| 名古屋鉄道 Nagoya Railroad | Japanese spelling;快速特急>特急>快速急行>急行>準急>普通 Rapid limited express > Limited express > Rapid express > Express > Semi-express > Ordinary |
| 阪神電鉄 Hanshin Electric Railway | Japanese spelling;快速特急>直通特急>特急>通勤特急>快速急行>快速>準急>普通 Rapid limited express > Direct limited express > Limited express > Commuter limited express > Rapid express > Rapid express > Semi-express > Normal |
Summary

This section explained the types of train operations in Japan and the differences between limited express, rapid, express, semi-express, and ordinary.
Limited express trains are recommended for those seeking comfort and time savings, while rapid trains are a convenient means of travel between regions. Express trains run even faster and reduce travel time. Semi-express trains are a convenient option for travel within a region, and ordinary trains are used by local people in their daily lives.
When boarding a train, make sure you know your destination and where the train stops.
Stops are different even for trains going in the same direction.
To enjoy more convenient train travel in Japan, it is important to have a good understanding of the different types of operation.